Cross Axis in Flexbox
In Flexbox, instead of directions like “up” and “down”, we use the concept of a cross axis.
This axis is used for vertical alignment of elements.
Illustration:
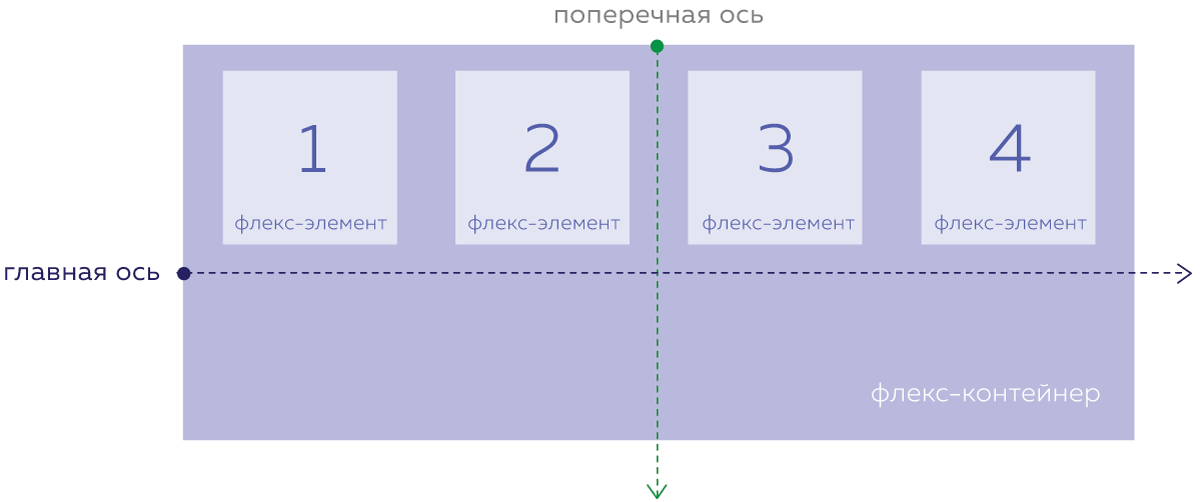
The cross axis is always perpendicular to the main axis and rotates with it:
- If the main axis is horizontal, the cross axis points downward.
- If the main axis is vertical, the cross axis points to the right.
This behavior may not feel intuitive at first, and takes some getting used to.
As a result, the cross axis is never pointing up or to the left.
Aligning along the Flexbox cross axis
The CSS property align-items defines how items are aligned along the cross axis.
Available values for align-items include:
stretch– Default value, stretches items to fill the full “height” of the flex container.
align-items: stretch;
flex-start– aligns items to the top of the container (in a row) or to the left (in a column).
align-items: flex-start;
flex-end– aligns items to the bottom edge along the cross axis.
align-items: flex-end;
center– centers items along the cross axis.
align-items: center;
baseline– aligns items along the baseline of their text. This line usually runs at the bottom of the letters.
align-items: baseline;
The align-self property
The align-self property allows you to individually align items on the cross axis.
Unlike alignment along the main axis, which is set for the entire container and applies equally to all items,
align-self lets you assign different alignment values to individual elements.
This property is applied directly to flex items and accepts the same values as align-items.
